Occupational & Environmental Lung Diseases Laboratory
R&D > Laboratories > Occupational & Environmental Lung Diseases Laboratory

Our Vision
The Laboratory of Occupational and Environmental Lung Diseases, located in the Tel Aviv Medical Center and affiliated to the Tel Aviv University, is the sole facility of its kind in Israel for studying environmental and occupational exposures and their effects on human health and disease. Exposomics detect the overall effective dose that induces injury and disease, and the lab focuses upon exposomics by performing biological monitoring. We use sputum induction and exhaled breath condensate by means of noninvasive techniques to retrieve sputum and condensate from the middle airways, in order to monitor past and recent exposures. OUR GOAL AND VISION ARE TO TRANSLATE OUR FINDINGS INTO NEW STRATEGIES FOR PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF PULMONARY DISEASES. In this context, we can bring the bench to the bedside to determine the causes of biological, environmental and occupational diseases.

Contact Us
Primary Investigators

Prof. Lizy Fireman, Lab PI
03-6947378 fireman@tlvmc.gov.il
General Contact

Mor Dahbash, MSc, Lab Manager
03 - 6947378 mord@tlvmc.gov.il
Address
Sammy Ofer Heart Building
Floor 10 Room 22

Research
(A) Percentile of ultrafine particles (UFP) in induced sputum (IS) samples and artificial stone dust (ASD) in exposed workers and non-exposed subjects.
(B) Particle size distribution (PSD) of ASD compared with natural stone.
(C) Percentile of UFP in IS samples of exposed workers versus non-exposed subjects.
PSD was evaluated by a Donner Tech Innovative Particle Analyzer (DIPA) analyser, and UFP were evaluated by a NanoSight LM20 in the sputum specimens and in the dust collected from an artificial stone factory. The y-axis represents the frequency for each size. *P<0.05 was considered significant by Mann-Whitney test. The results are ±SE of at least six independent experiments.
In the present project, we use an interventional method (“fitting test”) to personalize the use of the masks. The biological testing of nano-scaled particles will be done before and after the workers have learned and implemented the fitting test to maximize its effect.
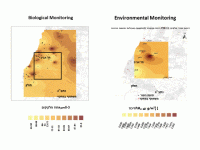
Our laboratory conducts research on biological monitoring by using biological samples (induced sputum and exhaled breath condensate) to measure particulate matter (PM) in the airways. The maps in the figure display completely different patterns when using data retrieved from biological monitoring vs environmental monitoring.
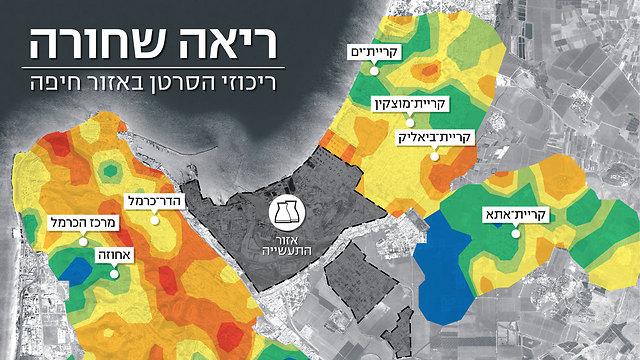
The goal of this project is to show the real pollution status in the Haifa Bay (compared to Tel Aviv metropolitan area), that can not be measured by environmental stations but rather by “human stations”.
Gallery








Our Team
Current Staff
- Prof. Lizy Fireman, Lab PI
- Mor Dahbash, MSc, Lab Manager
- Renan Lifshitz (MSc student)
- Sumia Abu Tuhama (MSc student)
Past Staff
Resident MD Students
- Alon Moscovich
- Akram Farid
- Iris Strul
- Ariel Meirowitz
PhD Students
- Iris Shahar
- Eran Levy
- Moshe Shtark
- Noa Ophir
MSc Students
- Tania Goldman
- Aya Lavi
- Emuna Shimoni
- Almog Sabanr
MD Students
- Tamir Weis
- Sahar Berger
- Talia Shahal
- Roni Gordon
Current funding



Highlight Publications
Fireman E, Mahamed AE, Rosengarten D, Noach Ophir N and Kramer MR.
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7237.
Association between elevated serum bilirubin levels with preserved lung function under conditions of exposure to air pollution.
Shapira U, Brezinski RY, Rogowski O, Zeltser D, Berliner S, Shapira I, Shenhar-Tsarfaty S, Fireman E. BMC Pulm Med 2021 Apr 13;21(1):119.
Gut G, Armoni Domany K, Sadot E, Soferman R, Fireman E, Sivan Y.Gut G, et al. J Asthma. 2020 Apr;57(4):366-372.
More Publications >>
Ultrafine particles in airways: a novel marker of COPD exacerbation risk and inflammatory status.
Fireman Klein E, Adir Y, Krencel A, Peri R, Vasserman B, Fireman E, Kessel A. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Mar 1;14:557-56
Klein EF, Adir Y, Fireman E, Kessel A. ERJ Open Res. 2020 Sep 14;6(3).
Ophir N, Bar Shai A, Korenstein R, Kramer MR, Fireman E. BMJ 2019 Dec;76(12):875-879.
Is induced sputum a useful noninvasive tool in the diagnosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis?
Baha A, Yıldırım F, Stark M, Kalkancı A, Fireman E, Köktürk N. Turk Thorac J. 2019 Aug 19;20(4):248-252.
Sputum anticitrullinated protein antibodies in patients with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis.
Polachek A, Vree Egberts W, Fireman E, Druckman I, Stark M, Paran D, Kaufman I, Wigler I, Levartovsky D, Caspi D, Pruijn GJM, Elkayam O. J Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Apr;24(3):122-126.
A novel combined score of biomarkers in sputum may be an indicator for lung cancer: A pilot study.
Bar-Shai A, Shenhar-Tsarfaty S, Ahimor A, Ophir N, Rotem M, Alcalay Y, Fireman E. Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Dec;487:139-144.2018.
Interstitial lung diseases associated with metal content in silicone breast implants: a case series.
Fireman E, Rosengarten D, Zelinger E, Kramer MR. Sarcoidosis Vasculitis and Diffuse Lung Diseases. 35: 381-389 2018.
Differential pattern of deposition of nanoparticles in the airways of exposed workers.
Fireman E, Edelheit R, Stark M, Bar Shai A. J Nanopart Res. 2017;19(2).
Fireman E, Alcalay Y, Ophir N, Kivity S, Stejskal V. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology. Mar 17, 2016 2: 00086.
Ophir N., Bar Shai A, Alkalay Y, Israeli S, Korenstein R ,Krermer M, Fireman E. ERJ Research March 17 2016 2:86
Mapping air pollution by biological monitoring in the Tel-Aviv metropolitan area.
Lavi A, Potchter O, Omer I, Fireman E. Int J Environ Health Res. 2015 Nov 24:1-15.
Bar-Shai A, Alcalay Y, Adi Sagiv, A Rotem M , Alon R, Fireman E. Respirology. 2015 Jun 10.
Ultrafine particle content in exhaled breath condensate in airways of asthmatic children.
Benor S, Alcalay Y, Armoni Domany K, Gut G, Soferman S, Kivity S, Fireman E. J Breath Res 2015 Apr 1;9(2).
Balmes JR, Abraham JL, Dweik RA, Fireman E, Fontenot AP, Maier LA, Muller-Quernheim J, Ostiguy G, Pepper LD, Saltini C, Schuler CR, Takaro TK, Wambach PF; ATS Ad Hoc Committee on Beryllium Sensitivity and Chronic Beryllium Disease .Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Nov 15;190(10(.
Fireman E, Bliznuk B, Schwarz Y, Soferman R, Kivity S. International Archives of Occupational Environmental Health 2014 Aug 20.
Fireman E, Lerman Y, Stark M, PardoA, Schwarz Y V. Van Dyke M, Jill Elliot J, Barkes B, Newman L, Maier L. Journal Occupational Environmental Hygiene 2014 Dec;11(12):809-18.
Biological exposure metrics of beryllium-exposed dental technicians.
Stark M, Lerman Y, Kapel A, Pardo A, Schwartz Y, Newman L, Maier L, Fireman E. Archives of Occupational Environmental Health 2014;69(2):89-99.
Chest wall shrapnel-induced chronic beryllium disease.
Fireman E, Bar Shai A, Lerman Y, Topilsky M, Blanc P, Maier L, Li L, Chandra S, Abraham JM, Fomin I, Aviram G, Abraham JL. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2012 Oct;29(2):147-50.