Immunology and Advanced CAR-T therapy
R&D > Laboratories > Immunology and Advanced CAR-T therapy

Our Vision
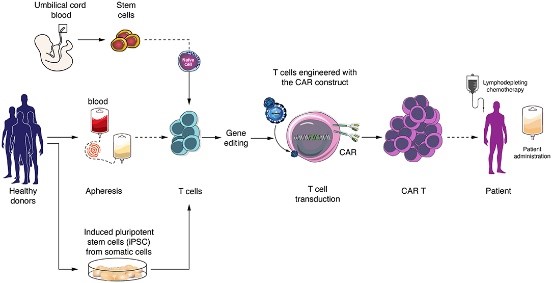
The Immunology and Advanced CAR-T therapy, has laid the fundamental groundwork for genetically engineering patients’ immune T cells against their own cancer, based on the recognition and execution of cancer cells by cytotoxic T cells. This is done by adding a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) to the T cells to recognize the cancerous cells. CAR-T are white blood T cells outfitted with receptors that specifically seek out and identify tumors, promoting their destruction. This novel treatment combines the advantages of two immune system components: antibodies, which are capable of recognizing tumors but cannot efficiently penetrate them, and T cells, which -in principle- can carve through cancerous tissue, but often lack the ability to recognize and home in on the tumor. Over the course of two decades, CAR-T cell technology transformed from a revolutionary idea that works in the lab to a feasible treatment that is effective and safe in patients. Today, the FDA has approved this technology to treat leukemia and lymphoma patients. However, solid tumors are still a challenge, as well as manufacturing the CAR-T in a more productive way and developing an off-the-shelf CAR-T product. Our lab is focused on producing many new CAR-T cells, with specific recognition, or dual recognition to cancer cells, as well as developing solutions for the current challenges in this era.

Contact Us
Primary Investigators

Dr. Anat Globerson Levin, Lab PI
The Dotan Center for Advanced Therapies03-6972503 anatgl@tlvmc.gov.il

Dr. Galit Horn, Lab manager
03-6972503 galithorn@tlvmc.gov.il
Address
Sammy Ofer Heart Building
10th floor Room 52-56

Research
CAR T-cell therapy has shown remarkable successes in fighting B-cell leukemias/lymphomas. Promising response rates are reported in patients treated with B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) CAR T cells for multiple myeloma. However, responses appear to be nondurable, highlighting the need to expand the repertoire of multiple myeloma–specific targets for immunotherapy and to generate new CAR T cells. We developed a “dual-CAR” targeting two multiple myeloma–associated antigens and explored its safety and efficacy. To reduce the “off-target” toxicity, we used the recognition of paired antigens that were co-expressed by the tumor to induce efficient CAR T-cell activation. Our findings indicated that the dual CAR T may provide a potent and safe alternative |
therapy for patients with multiple myeloma. This CAR T, which was developed at TASMC, is heading in the near future into a clinical trial that will performed by our new I-ACT (Ichilov-adaptive cell therapy) facility. This project is in collaboration with the Hemato-oncology department.
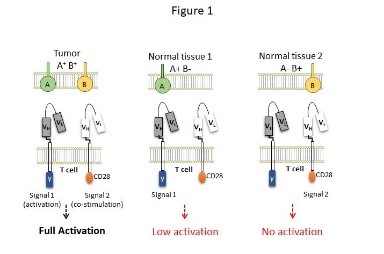
High-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC) is a type of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). EOC is the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death in women in the developed world and the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancies. EOC is often diagnosed at advanced-stage disease with an overall 5-year survival rate of <40%. While a significant progress has been made in surgical and chemotherapeutic treatments for EOC, the survival rates for this disease have only modestly improved. We constructed a ‘dual-Chimeric Antigen Receptor’ (dCAR) for ovarian cancer. The dCAR represents a new approach that addresses the major challenge of ‘off-tumor on-target’ toxicity in CAR therapy, namely, the risk of damage to healthy tissues of the patient, which express the target antigen of the selected CAR. The underlying idea is that restricting the activity of CAR T cells against a combination of two antigens, which are co-expressed by the tumor, but not by normal tissues, can prevent off target toxicity. We analyzed the potential efficacy and safety of the dual CAR in vitro. Additionally, we compared the administration of CAR T cells locally to intravenous injection and compared it to IV injections. We show that intra- tumoral injection have a significantly superior effect in vivo. This project is in collaboration with the Gyno-oncology department.
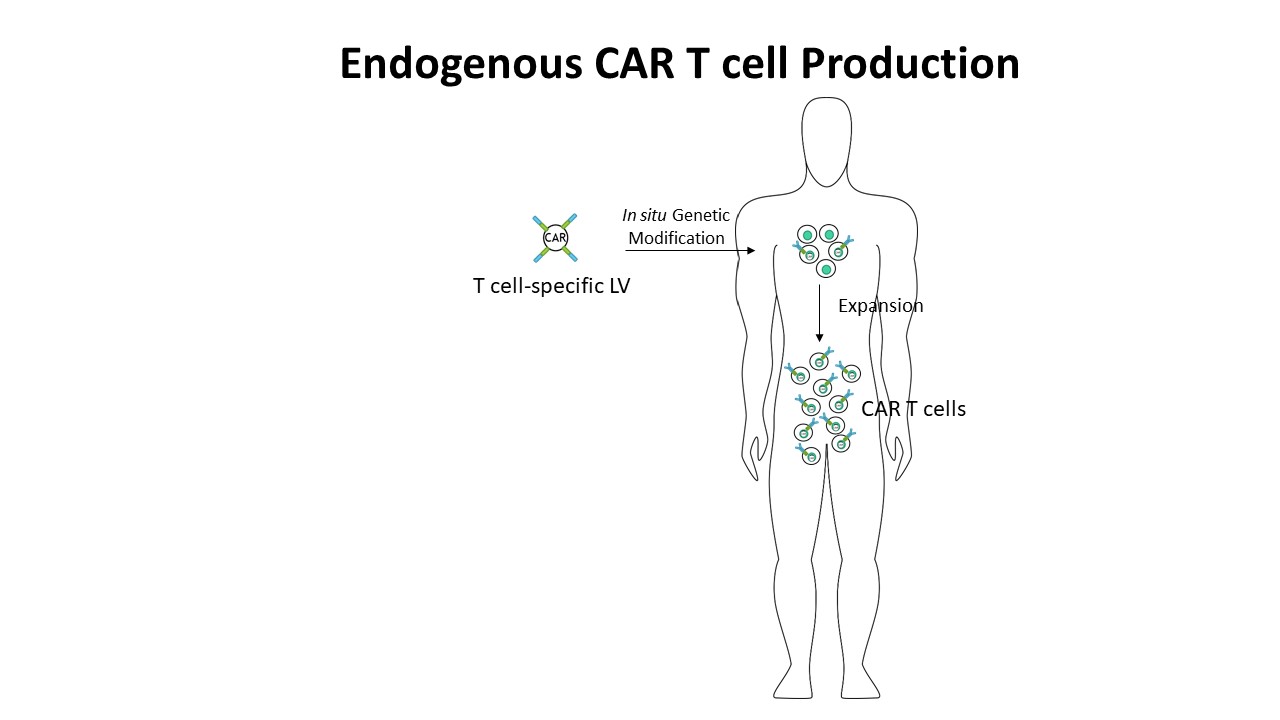
The challenges of CAR T cells manufacturing are that they are highly expensive and labor demanding as well as a personalized therapy treatment. We developed a lentiviral drug genetically reprogramming and redirecting endogenous T cells toward tumors. This aims for a Universal “off-the-shelf” CAR T cell approach that can be delivered to a large population of cancer patients with minimal cost and high efficiency by in situ redirecting endogenous T cells. This project is in collaboration with the MDA, USA. |
One of the main challenges of CAR T cells today, is infiltration to the solid tumor microenvironment and attacking the whole cancer tissue. EVs obtained from CAR T cells contain similar profile as their parental cells. Specifically, isolated EVs derived from T-cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) toward the antigen of interest, and contained cytokine and enzymes, bind to and penetrate into specific tumor cells, induce apoptosis and there by provide outstanding anti-cancer effects. As for their small size, we believe that CAR-T EVs’ may enable penetration to solid tumors and induce specific cytotoxicity against tumor cells while minimizing cytokine storm. Using CAR T EVs rather than CAR-T cells may provide an immunotherapeutic approach that may reach solid tumors, and improve therapeutic efficacy while reducing costs and risks. This project is in collaboration with the Hematology research Lab. |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant in patients with malignant hematological diseases is challenging for treatment. We developed with Cell Source, in a collaboration between Prof. Yair Reisner, Prof. Zelig Eshhar & Dr. Anat Globerson Levin, a similar approach to the allogeneic “off-the shelf” transplantation, combined with CAR T cells targeting the cancer, which is currently shown to be a success in preclinical mouse models, and will be tested in the near future at MD Anderson in relapsing patients with malignant hematological diseases
Gallery












Our Team
Current Staff
Researchers
- Galit Horn, PhD
- Kenneth Hollander, PhD
- Moran Rawet Slobodkin, PhD
- Einav Hubel-Manor, PhD
Students
- Ester Buderovsky, PhD Student
- Omer Azar, MD-PhD Student
- Veronika Lerman, MSc student
- Shir Katan, MSc student
- Tamar Baruch, MSc student
- Daniel Arazi, MSc student
- Guy Avivi, MSc student
Consultant
- Tova Waks
- Zelig Eshhar, PhD, lab founder
Administrative
- Michal Hecht
Collaborators
- Amer Najjar, MDA, USA
- Yair Reisner, WIZ/MDA
- Vladimir Vainstein, Hadassah
- Natalie Kalev Kronik, Hadassah
- Irit Avivi, TASMC
- Anat Aharon, TASMC
- Yael Cohen, TASMC
- Benzi Katz, TASMC
- Dan Grisaru, TASMC
- Ido Laskov, TASMC
- Yael Raz, TASMC
- Vered Padler-Karavani, TAU
- Eilon Sherman, HUJI
- Yankel Gabet, TAU
- Ido Wolf, TASMC
- Tami Rubinek, TASMC
Past Staff
Researchers
- Gidi Gross, PhD
- David Steiner, PhD
- Tamar Shiloach, PhD
- Aviad Pato, PhD
- Moran Rawet Slobodkin, PhD
- Lihi Ninio Many, PhD
- Ziv Itach Abromovitch, MSc
- Shaked Almog, MSc
- Shahar Barami, Rom student
- Sahar Laros, Rom student
Current funding








Highlight Publications
The Clinical Significance of Circulating Lymphocytes Morphology in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma As Determined by a Novel, Highly Sensitive Microscopy, Fridberg, G.; Horn, G.; Globerson Levin, A.; Benisty, D.; Kay, S.; Glait-Santar, C.; Perry, C.; Ram, R.; Avivi, I.; Katz, B.-Z. Cancers 2023, 15, 5611. |
Nanoscale CAR Organization at the Immune Synapse Correlates with CAR-T Effector Functions, Cells. Julia Sajman, Oren Yakovian, Naamit Unger Deshet, Shaked Almog, Galit Horn, Tova Waks , Anat Globerson Levin, Eilon Sherman. 2023 Sep 12;12(18):2261 |
Deshet-Unger N, Horn G, Rawet-Slobodkin M, Waks T, Laskov I, Michaan N, Raz Y, Bar V, Zundelevich A, Aharon S, Turovsky L, Mallel G, Salpeter S, Neev G, Hollander KS, Katz BZ, Grisaru D*, Globerson Levin A*. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2216. |
Extracellular vesicles derived from CAR-T Cells: A potential therapy for cancer Anat Aharon, Galit Horn , Tali Hana Bar-Lev , Einav Zagagi Yohay , Tova Waks , Maya Levin , Naamit Deshet Unger , Irit Avivi , Anat Globerson Levin. Hum Gene Ther . 2021 Sep 8. Hum Gene Ther . 2021 Sep 8. |
CAR T cells: building on the CD19 paradigm, Globerson Levin A, Eshhar Z, Rivière I, Sadelain M., Eur J Immunol 2021. |
T cells retain pivotal anti tumoral functions under tumor treating fields (TTFields), Diamant G, Simchony H, Gasri Plotnitsky L, Roitman M, Shiloach T, Globerson Levin A, Eshhar Z, Oz H, Pencovich N, Grossman R, Ram Z, Volovitz I. J Immunol 2021 Jul |
Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) for BTK Efficiently Inhibit B-cell Receptor Signaling and Can Overcome Ibrutinib Resistance in CLL cells, Yamit Shorer Arbel, Ben-Zion Katz, Ronen Gabizon, Amit Shraga, Yotam Bronstein, Talia Kamdjou, Chava Perry, Anat Globerson Levin, Irit Avivi, Nir London, Yair Herishanu, Frontiers in Oncology Pub Date : 2021-03-30, Front. Oncol., 13 May 2021 |
More Publications >>
P32-specific CAR T cells with dual antitumor and antiangiogenic therapeutic potential in gliomas, Liat Rousso-Noori, Ignacio Mastandrea, Shauli Talmor, Tova Waks, Anat Globerson Levin, Maarja Haugas, Tambet Teesalu, Luis Alvarez-Vallina, Zelig Eshhar, and Dinorah Friedmann-Morvinski, Nature Communications 12 (1), 1-13, June 2021 |
Shaping Functional Avidity of CAR-T Cells: Affinity, Avidity and Antigen Density that Regulate Response. , Greenman R, Pizam Y, Haus-Cohen M, Goor A, Horev G, Denkberg G, Sinik K, Elbaz Y, Bronner V, Globerson Levin A, Horn G, Shen-Orr S, Reiter Y. , Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Mar 1
Treatment of Multiple Myeloma using Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells with Dual Specificity, Anat Globerson Levin, Moran Rawet Slobodkin, Tova Waks, Galit Horn, Lihi Ninio-Many, Naamit Deshet Unger, Yaara Ohayon, Shimrit Suliman, Yael Cohen, Boris Tartakovsky, Ella Naparstek, Irit Avivi, Zelig Eshhar, Cancer Immunol Res 2020 Oct 2, .2020. |
Less is more: reducing the number of administered Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells in a mouse model using a mathematically guided approach, Anat Globerson Levin, Natalie Kronik, Tamar Shiloach, Tova Waks, Zelig Eshhar, Vladimir Vainstein, Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (CII), Febrary 2020
Nanoparticulate vaccine inhibits tumor growth via improved T cell recruitment into melanoma and huHER2 breast cancer. Zupančič E, Curato C, Kim JS, Yeini E, Porat Z, Viana AS, Globerson Levin A, Waks T, Eshhar Z, Moreira JN, Satchi-Fainaro R, Eisenbach L, Jung S, Florindo HF. Nanomedicine. 2018 Jan 3. pii: S1549-9634(17)30589-0. |
HER2-Targeted Polyinosine/Polycytosine Therapy Inhibits Tumor Growth and Modulates the Tumor Immune Microenvironment, Zigler M, Shir A, Joubran S, Sagalov A, Klein S, Edinger N, Lau J, Yu SF, Mizraji G, Globerson Levin A, Sliwkowski MX, Levitzki A. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Aug;4(8):688-97. |